One of the software tools that I find a lot of people talking about these days is DeNoise from Topaz. I have never been terribly bothered by noise in my images. Modern cameras do a pretty remarkable job of handling noise and, for most usage purposes, the noise is not really an issue if it is there. I have posted my efforts with PureRAW in its various forms where I have tried it out to see how the noise reduction comes out and, while I have seen strengths and weaknesses in it, I have never seen it as something I needed to spend on.
One of the software tools that I find a lot of people talking about these days is DeNoise from Topaz. I have never been terribly bothered by noise in my images. Modern cameras do a pretty remarkable job of handling noise and, for most usage purposes, the noise is not really an issue if it is there. I have posted my efforts with PureRAW in its various forms where I have tried it out to see how the noise reduction comes out and, while I have seen strengths and weaknesses in it, I have never seen it as something I needed to spend on.
 Lightroom Classic had one of its periodic updates recently. The big new feature was their own denoise functionality. Much like my experimentation with PureRAW, it analyzes the shot and creates a new DNG file with the noise suppressed. I was curious to see how it would perform and, seeing as it is included in the price of my subscription, I have it anyway. I decided to take some shots I had recently used for the PureRAW3 trial I had done and compare with the Lightroom version.
Lightroom Classic had one of its periodic updates recently. The big new feature was their own denoise functionality. Much like my experimentation with PureRAW, it analyzes the shot and creates a new DNG file with the noise suppressed. I was curious to see how it would perform and, seeing as it is included in the price of my subscription, I have it anyway. I decided to take some shots I had recently used for the PureRAW3 trial I had done and compare with the Lightroom version.
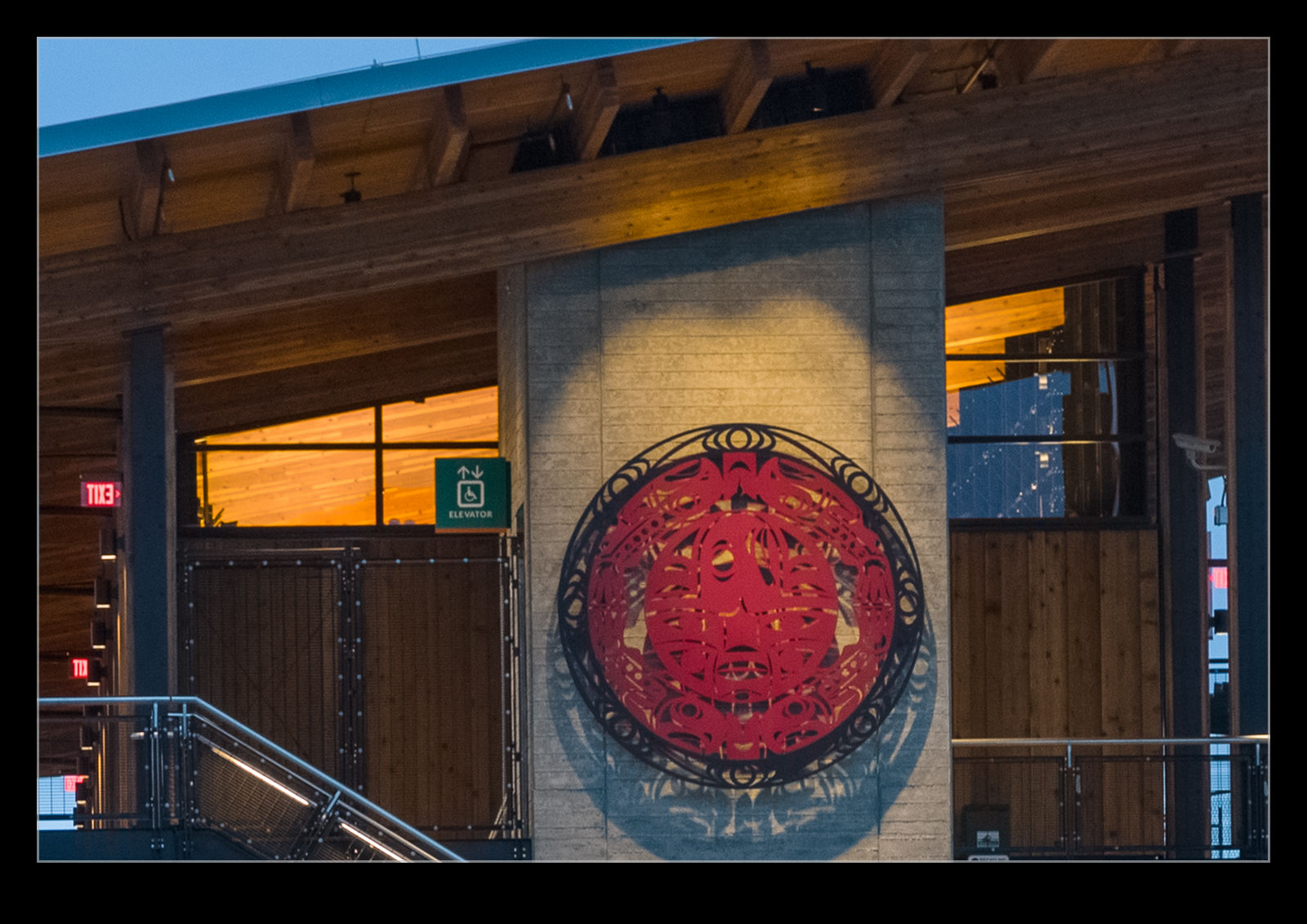
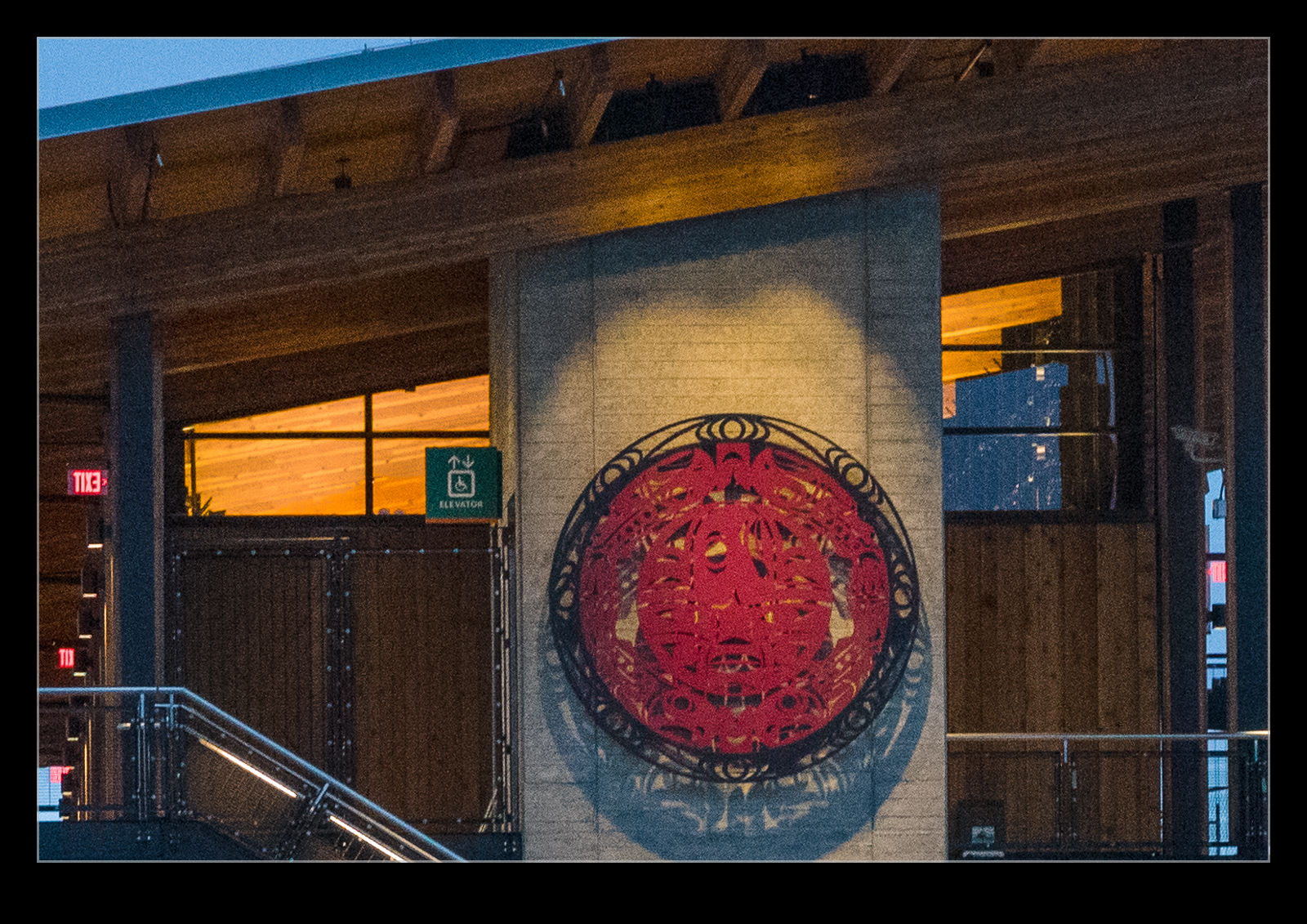
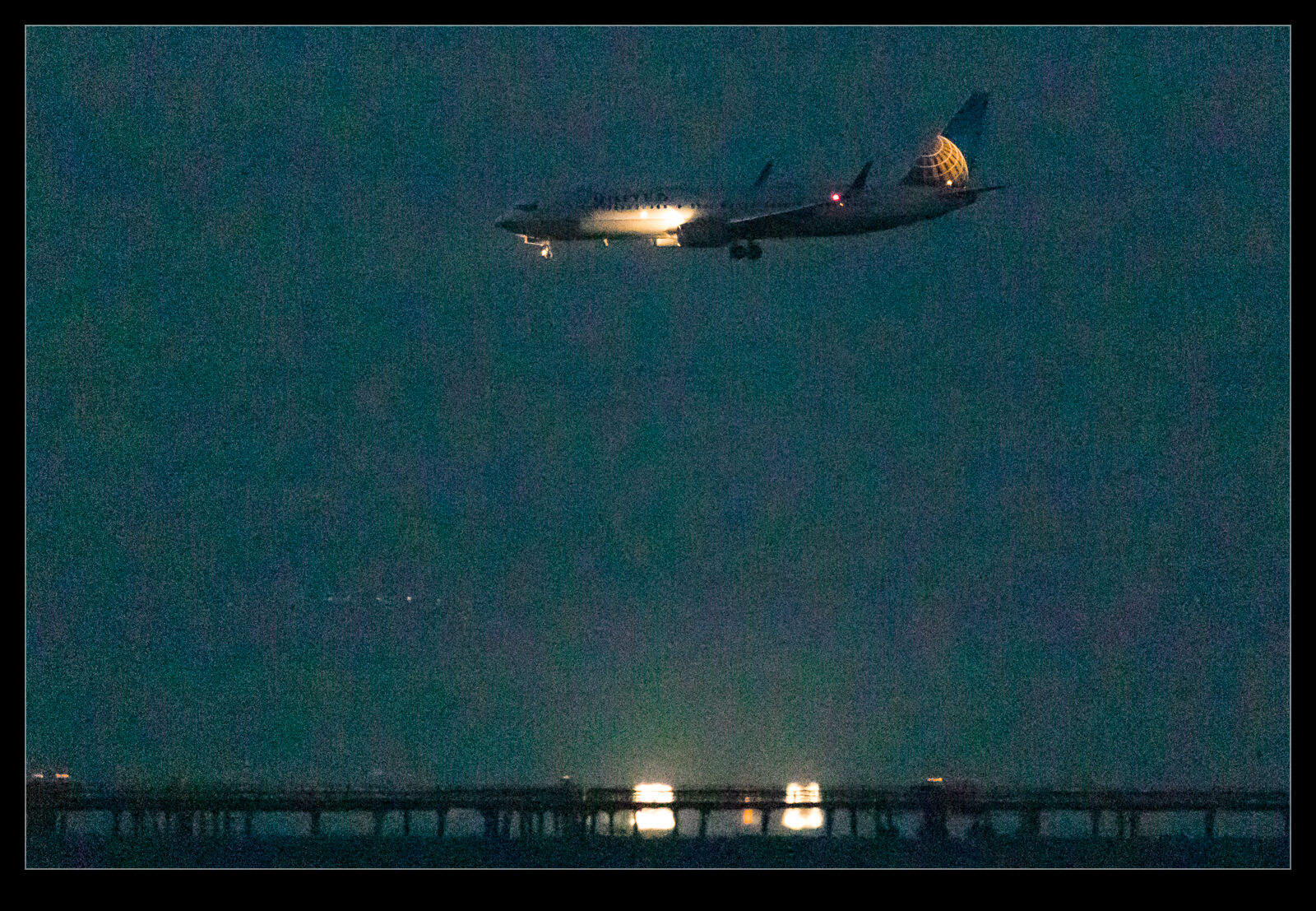
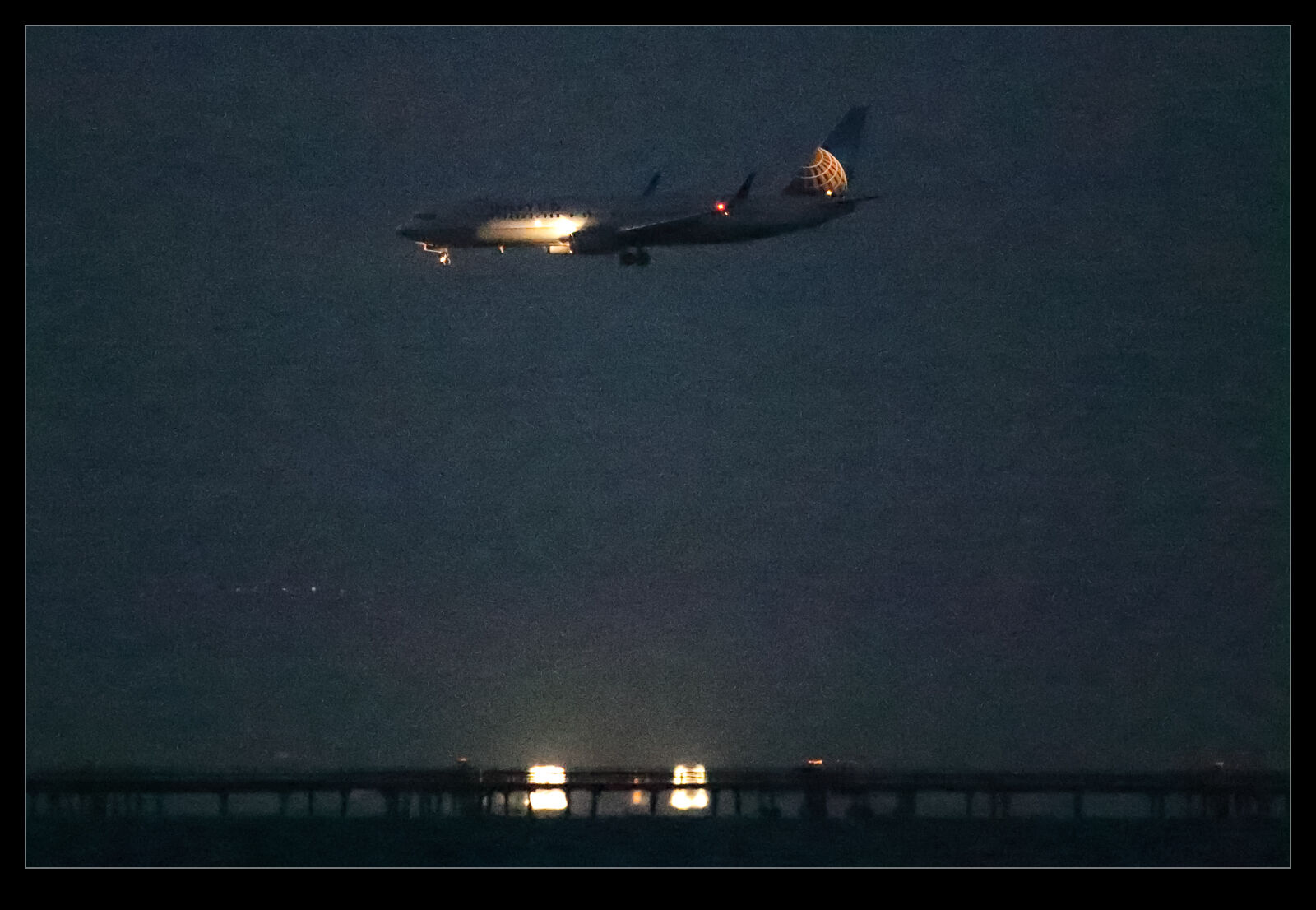
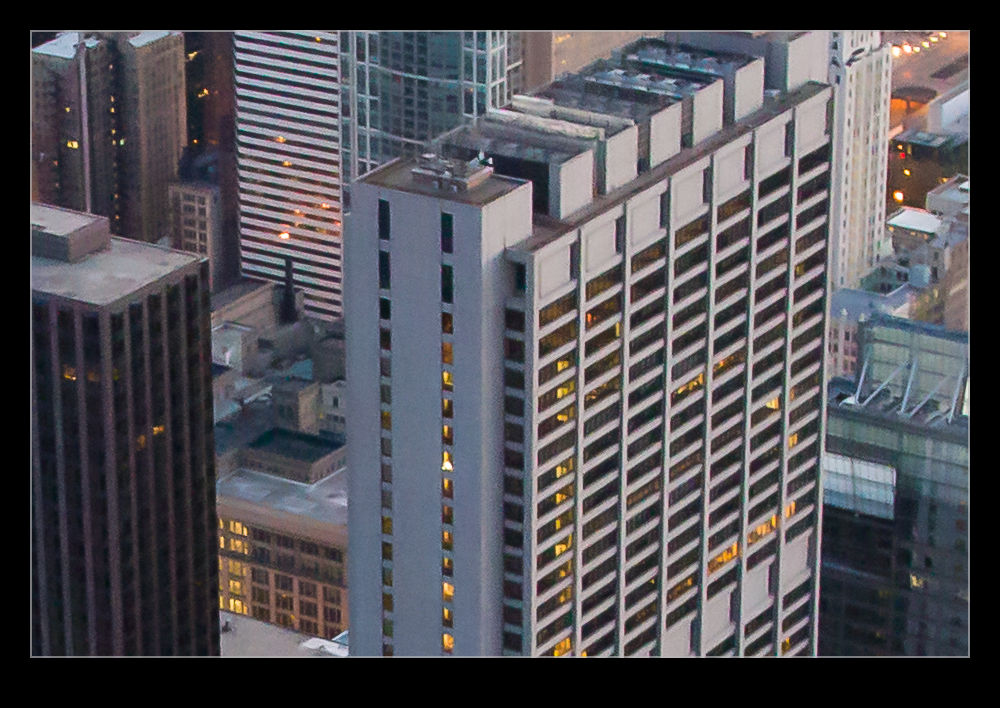
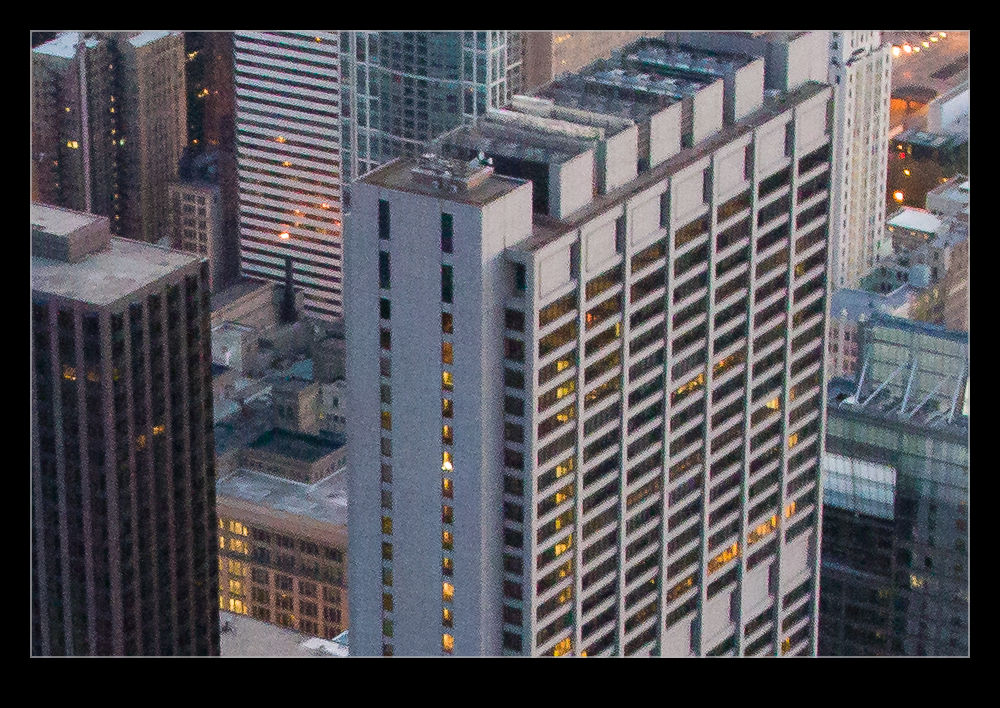
 It defaulted to a 50 level of noise reduction. I don’t know whether this is a percentage and what of but it is a scale so I played with it. I did some at 50 and some at 75 to see whether more aggressive noise reduction had detrimental effects on other parts of the image. Comparing these things and then sharing the results is a touch tricky so I have created a single image from four layers. They are the original Lightroom develop settings, the PureRAW3 version, the 75 denoise settings and the 50 denoise settings. I mask them to make the image into four sections. Then, to make it useful on here, I have zoomed in to show the borders between them to provide some sort of comparison.
It defaulted to a 50 level of noise reduction. I don’t know whether this is a percentage and what of but it is a scale so I played with it. I did some at 50 and some at 75 to see whether more aggressive noise reduction had detrimental effects on other parts of the image. Comparing these things and then sharing the results is a touch tricky so I have created a single image from four layers. They are the original Lightroom develop settings, the PureRAW3 version, the 75 denoise settings and the 50 denoise settings. I mask them to make the image into four sections. Then, to make it useful on here, I have zoomed in to show the borders between them to provide some sort of comparison.
The PureRAW3 result is very aggressive on noise reduction. However, I find it can make some odd artifacts in the images where details were not that clear to begin with. The 75 setting in Lightroom provided a very similar level of noise reduction to PureRAW3. It is slightly noisier but barely enough to matter. A setting of 50 does show more noise. It is still a significant improvement over the basic Camera Raw settings and very usable.
What do I conclude from all of this? First, as I have said before when testing the PureRAW trials, it provides some interesting results but it is not relevant to enough of my work to matter to me sufficient for me to spend a bunch of money on buying it. Having denoise in Lightroom now provides me with a very similar option but within the existing price I am paying for Lightroom. Therefore, I will make use of it when the situation dictates. It would be a regular part of my workflow because really high ISO shots are only an occasional thing for me but having it there when I want it will be handy.