 As I posted a while ago, I have been experimenting with stitching shots from my phone. Since I am shooting in raw on the phone, I have some latitude to play with the shots in post that wasn’t there before. This time, though, I thought about it a bit more and put the camera into manual mode to fix the exposure. This should make the stitching and blending easier than when it changed between shots (although, to give the Lightroom team credit, it did a pretty good job anyway). I allowed plenty of overlap and the merge seemed to go pretty well. Since it outputs a dng file, you still have the chance to edit more aggressively than would be possible with a jpeg. Meanwhile, you get a higher resolution shot than with the internal pano mode. This may be my go to method from now on.
As I posted a while ago, I have been experimenting with stitching shots from my phone. Since I am shooting in raw on the phone, I have some latitude to play with the shots in post that wasn’t there before. This time, though, I thought about it a bit more and put the camera into manual mode to fix the exposure. This should make the stitching and blending easier than when it changed between shots (although, to give the Lightroom team credit, it did a pretty good job anyway). I allowed plenty of overlap and the merge seemed to go pretty well. Since it outputs a dng file, you still have the chance to edit more aggressively than would be possible with a jpeg. Meanwhile, you get a higher resolution shot than with the internal pano mode. This may be my go to method from now on.
Tag Archives: technique
Sacramento Roundhouse
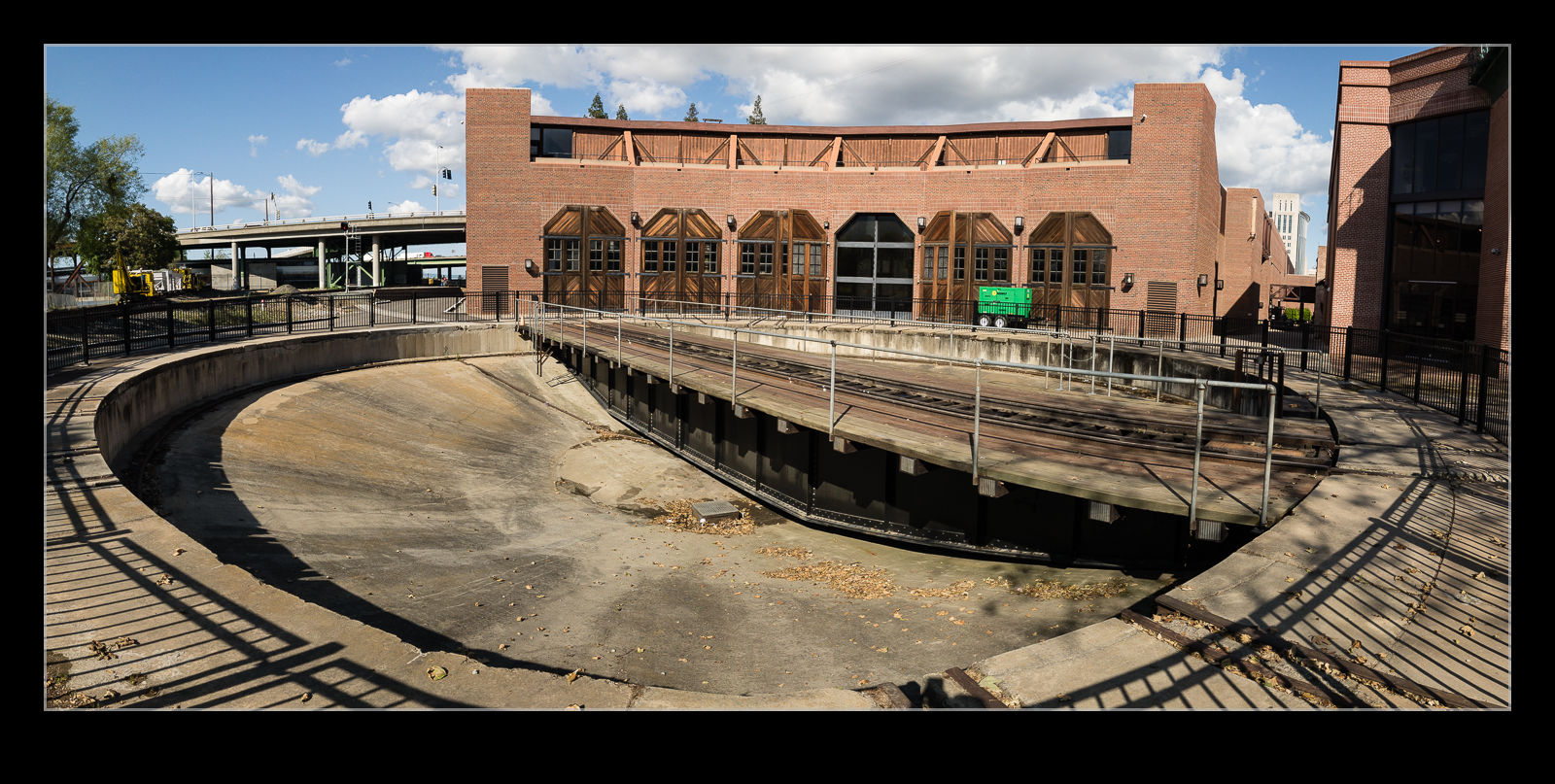 One end of the railroad museum in Sacramento is a roundhouse. It is accessible still from the line outside and I was there for a modern locomotive that was being unveiled. Access comes via a turntable which sits right next to the path along the river. I figured I would put together a panorama of the scene. However, I only had my phone (albeit able to shoot raw). I had never tried shooting a pano sequence with it before having only used its internal pano function.
One end of the railroad museum in Sacramento is a roundhouse. It is accessible still from the line outside and I was there for a modern locomotive that was being unveiled. Access comes via a turntable which sits right next to the path along the river. I figured I would put together a panorama of the scene. However, I only had my phone (albeit able to shoot raw). I had never tried shooting a pano sequence with it before having only used its internal pano function.
I wasn’t controlling the exposure (although there is a manual function in the app I use) but I had noticed that the Lightroom pano function seemed quite adept at dealing with small exposure variation. I took the sequence and there was not a big difference across them. When I got home, I added them to Lightroom and had a go at the stitching function. It worked better than I had expected. Some small distortions were there but it actually was rather good. I had not been happy about the reduced size of the pano function of the phone so this has provided a better option to use in the future.
Shooting RAW on the Phone
The update to iOS 10 brought with it the possibility to shoot in RAW on the iPhone. For some reason Apple didn’t bother to incorporate this feature in the base phone app but they did make it available to other camera app developers. Camera+ is one that I use a bit so I figured I would start shooting in RAW via that. Obviously RAW means larger files but, since I download my files to the desktop frequently and tend to clear out the phone, this wasn’t a concern.
First thing I found out was that other apps could see the shots. I had taken a few shots and wanted to upload to Facebook and it turned out there wasn’t a problem doing so. However, the main benefit was anticipated to post processing back on the desktop. With the SLR shots (is there any point to saying DSLR these days?), it is possible to recover a lot from the highlights and shadows. Would the same be possible with the phone? Sort of. You can get a bit more in these areas than would be the case with the JPEG when things are quickly lost. However, the sensor data is still not anywhere close to being as adaptable as it is for an SLR. You get more flexibility to pull the sky back but it is still pretty limited.
Is it worth using? Definitely. While it might not be the post processing experience you will be used to with SLR files, it is certainly better than the JPEGs provide. The increase in file size is hardly an issue these days so I will using it from now on. The camera app doesn’t have the pan and time lapse stuff so easily to hand so the phone’s base app will still get used but, aside from that, it will be my choice. My main gripe now is that they have a random file naming protocol that is a little difficult to get used to. Small problems, eh?
Sound for the Videos
While I have experimented with video a fair bit over time, one thing I haven’t done is put together a video with a presenter in it. My mum was recently staying and she had an idea for something she wanted to do that involved her doing a presentation on video that could be shared at a later date. My own experience and some information I had seen online made me think that the key to getting a good result was not going to be the video but was instead the sound. The microphone on the camera is of okay quality but it picks up the sound of everything around it. The voice is isolated and any video online that does not take a careful approach to audio is very obvious and sounds decidedly amateurish.
The ideal solution would be to have lav mikes, the small mike you see attached to the clothing of TV presenters. These are actually pretty accessible and cheap but I didn’t have the time to sort something out. However, a surprisingly good alternative was readily to hand. I have an app on my phone for sound recording which I use when interviewing people for articles. Instead of using the plugin microphone, I used the headphone/microphone cable. By running it inside the clothing and just leaving the microphone up near my mum’s throat, we were able to make a very good sound recording. The closeness of the mike to her mouth meant the sound was very localized and clear so the background noise was lost. The room we used did not have bad echoes either so the audio ended up being pretty clear.
Then it was just a case of having a conspicuous clap on the audio track and the video file to allow me to synch the sound and audio together and we were off to the races. I shot everything with two cameras – one head on and one from the side – with the idea of cutting between them. However, when I did the first edit, the side camera didn’t seem to fit with the style of presenting to camera. I imagine it works better for an interview style piece. I reverted to the head on shot with some images cut in periodically to illustrate the piece. Overall, it worked pretty well. We did a number of takes and mum got progressively more relaxed in each one. I had thought I might cut the best bits together but the final take was really good so I didn’t need to do so. I hope her audience likes the result.
Trying to Remove the Traffic on the Bridge
The suspension bridge at Lions Gate in Stanley Park, Vancouver is a magnet for photographers. I was only passing through but, as we watched the traffic moving across the bridge, I was thinking about how to get a shot that didn’t have cars on it. The traffic was steady so there was not way I would get a clear moment. Indeed, while we were there, they changed the lights and reversed the center lane based on the traffic demand.
I didn’t have a tripod but I did decide to experiment with an alternative technique. This is best done using a tripod and a lot of exposures but I figured I would go with shots that were pretty closely aligned and about half a dozen shots. This didn’t work perfectly but it didn’t go too badly. When you get back to the computer, you open up Photoshop. Click on File and Statistics and a dialog opens up. Select all of the files and change the option at the top to Median and check Align Images. Then send it on its way.
 If the shots are good and there are enough, the algorithm will look at each shot and see the changing items – cars in this case – as the oddities. It will see what is consistent in each shot and get rid of the odd stuff. If you have it right, the cars will vanish. In this case, there were some overlaps and not enough shots but it still did a reasonable job.
If the shots are good and there are enough, the algorithm will look at each shot and see the changing items – cars in this case – as the oddities. It will see what is consistent in each shot and get rid of the odd stuff. If you have it right, the cars will vanish. In this case, there were some overlaps and not enough shots but it still did a reasonable job.
Polarizer Comparison
When I changed bodies, I had to update some of my accessories too. My old filter system was fine on a cropped body but with full frame, the filter holder encroached on the corners for the wide angle lenses. I took the opportunity to change my polarizer set up. I used to use a polarizer on my Cokin holder. This was a bit inconvenient when I was using lens hoods. Instead, I decided to get a screw in polarizer. Since most of my lenses have the same filter size, this gives me more flexibility.
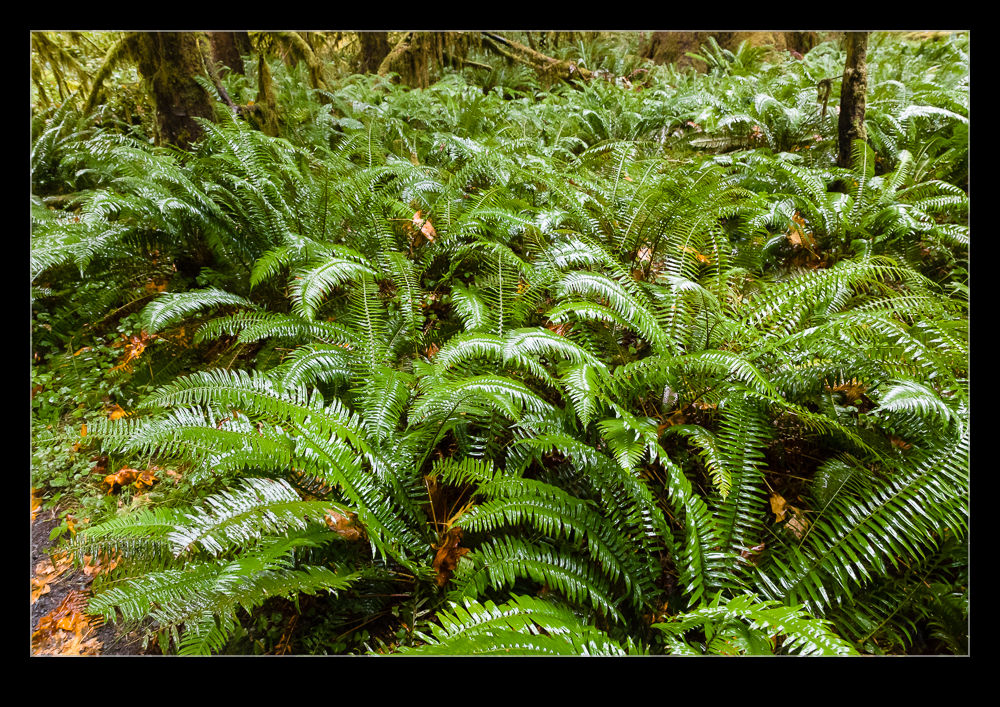
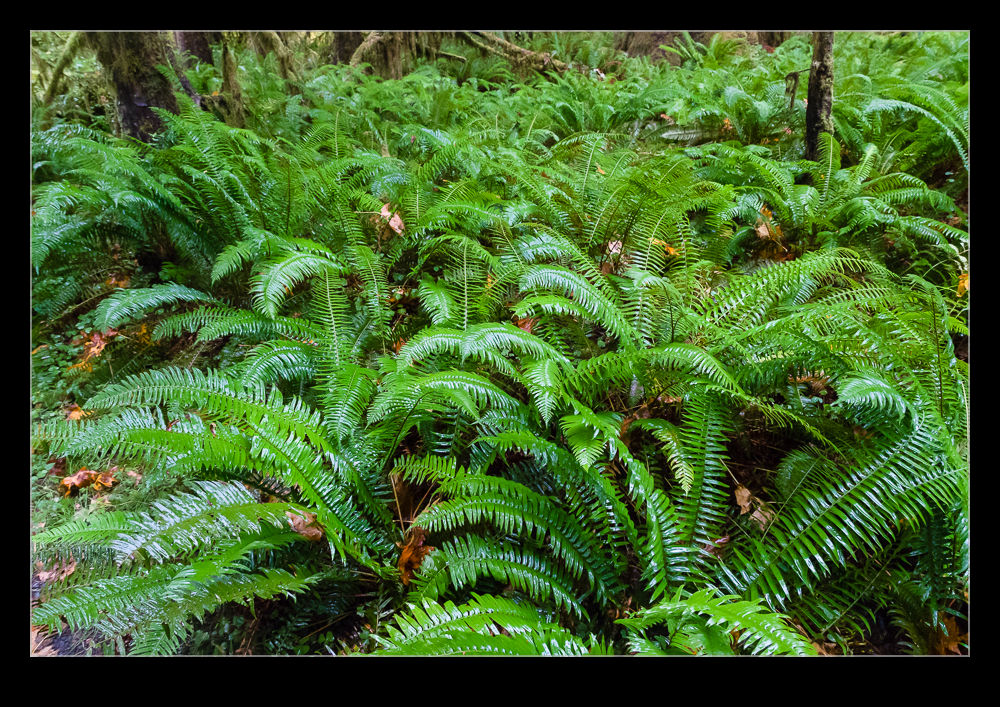
 I took the polarizer with me on vacation. One place where I made good use of it was in the rain forest. While it was pretty dark in the heavy forest cover, there was moisture everywhere and this meant a lot of reflections and glare. Consequently, I went with the polarizer most of the time. While I was there, though, I decided to do some experimentation by repeating some shots without the polarizer to see how much of a difference it made. You can see the with and without shots here and judge for yourself what a difference it makes.
I took the polarizer with me on vacation. One place where I made good use of it was in the rain forest. While it was pretty dark in the heavy forest cover, there was moisture everywhere and this meant a lot of reflections and glare. Consequently, I went with the polarizer most of the time. While I was there, though, I decided to do some experimentation by repeating some shots without the polarizer to see how much of a difference it made. You can see the with and without shots here and judge for yourself what a difference it makes.
High ISO Raw File Size
On my previous camera bodies I had occasionally shot at very high ISO settings as a result of the lack of light. I had not paid a huge amount of attention to any secondary effects of doing so. My current cameras had a work out in some very low light when I decided to test them in some rather unfriendly conditions. When I was at home, I was running some disc backups and I found I could not get the normal number of files onto a single disc. A quick bit of investigation and I could see why. The high ISO shots had a significant increase in file size. As I understand it, RAW files, while containing all of the data from the sensor, do have an amount of compression applied. I imagine that the noise inherent in high ISO shots means that the compression is less effective as there is so much variation across pixels. As an example, a shot at ISO 320 will average at about 22Mb. The shots at ISO 51,200 are coming in at over 30Mb. At ISO 204,000, the files can hit 40Mb. That is quite an increase! Something to keep in mind when planning to shoot in very low light conditions.
Lightning Photography
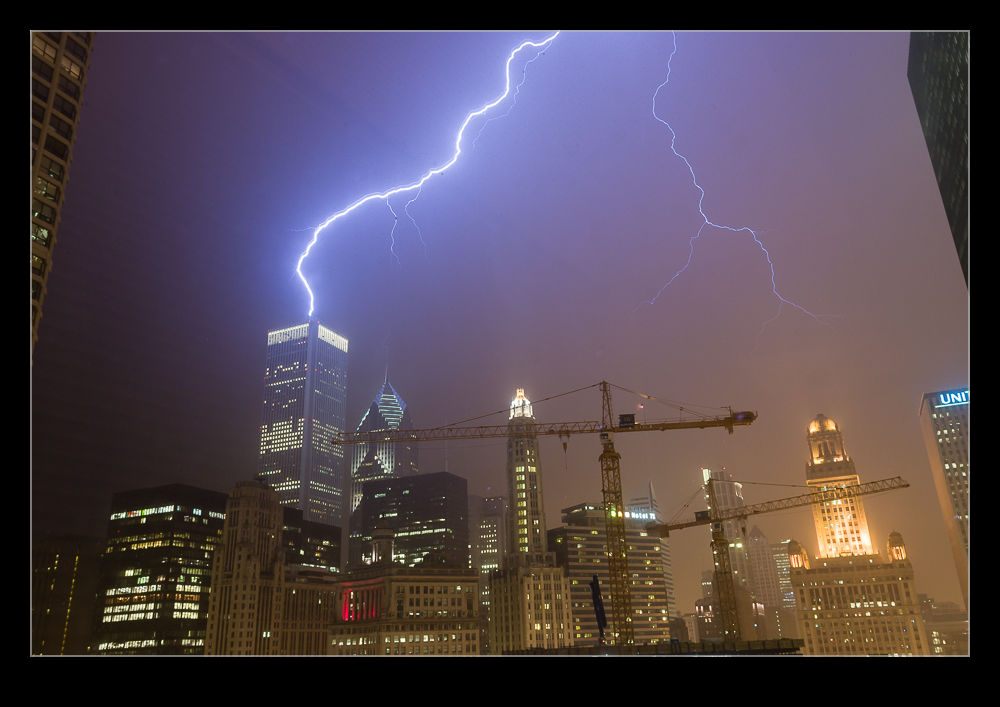 When I shot film I had a go at shooting lightning a number of times but never with any success. I would try and react to get the bolt but it was always gone. When you are using film and having a very low success rate, things get too expensive. Consequently, I gave up on it. The move to digital opened up a new range of possibilities.
When I shot film I had a go at shooting lightning a number of times but never with any success. I would try and react to get the bolt but it was always gone. When you are using film and having a very low success rate, things get too expensive. Consequently, I gave up on it. The move to digital opened up a new range of possibilities.
My new approach doesn’t involve much skill (but then neither does using an electronic trigger). I set up the exposure to have a reasonably long shutter speed. Then I put the camera on continuous mode, plug in the cable release and lock the shutter open. Then the camera takes a steady stream of shots. Of course, when there is a slight gap between shots, you can imagine when the lightning will strike.
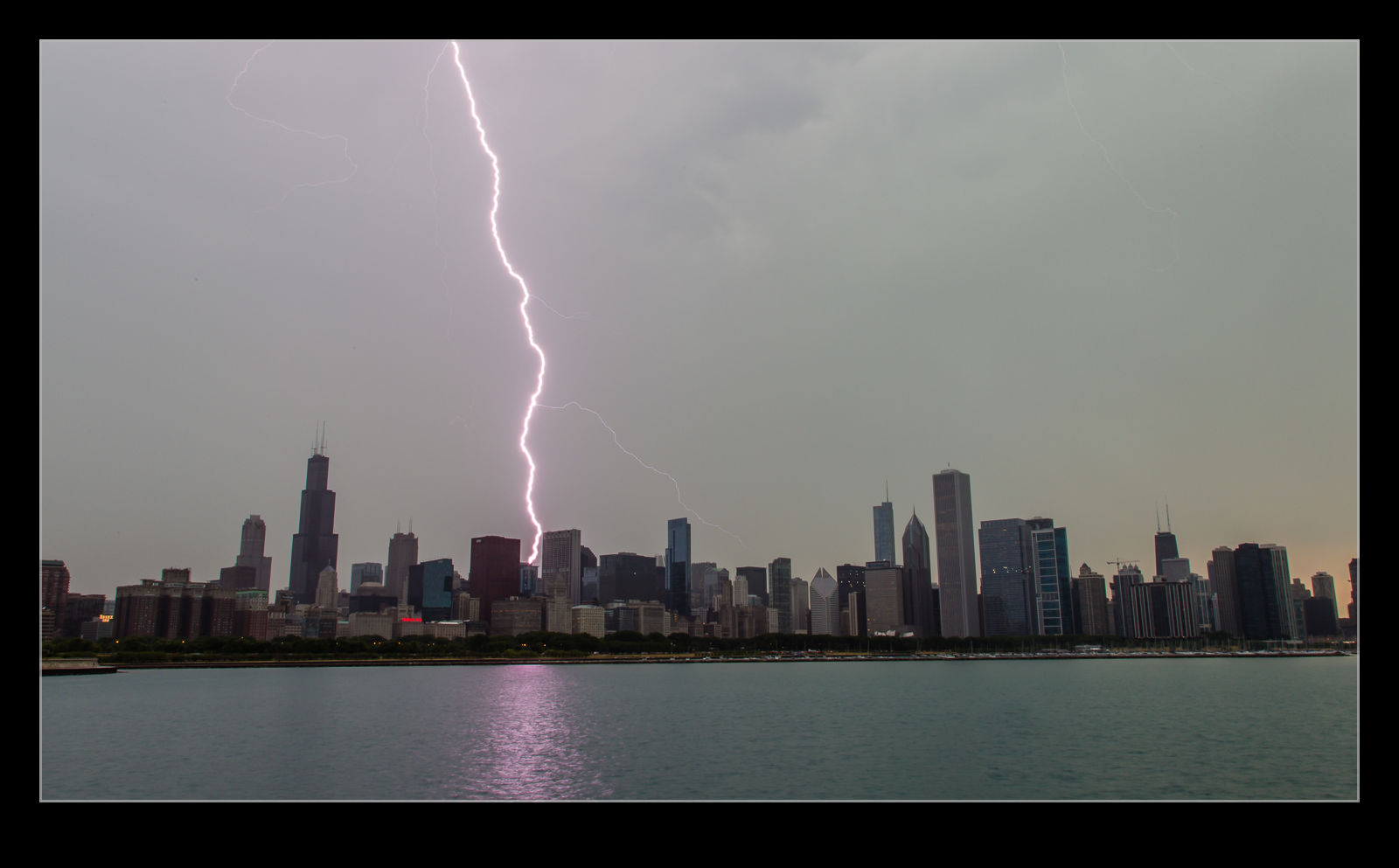 I used to shoot a lot from the apartment in Chicago. Set the camera up and go and do something else. Unfortunately, the heavy rains that would accompany the storm activity could result in the sky glaring out but you still had a chance. Some of the shots were okay and every once in a while you would get a really cool outcome. The Trump Tower was next to us and it would be struck occasionally but it was too close to get a good look at. You could hear it though!
I used to shoot a lot from the apartment in Chicago. Set the camera up and go and do something else. Unfortunately, the heavy rains that would accompany the storm activity could result in the sky glaring out but you still had a chance. Some of the shots were okay and every once in a while you would get a really cool outcome. The Trump Tower was next to us and it would be struck occasionally but it was too close to get a good look at. You could hear it though!
Crosswind Training in the Citabria
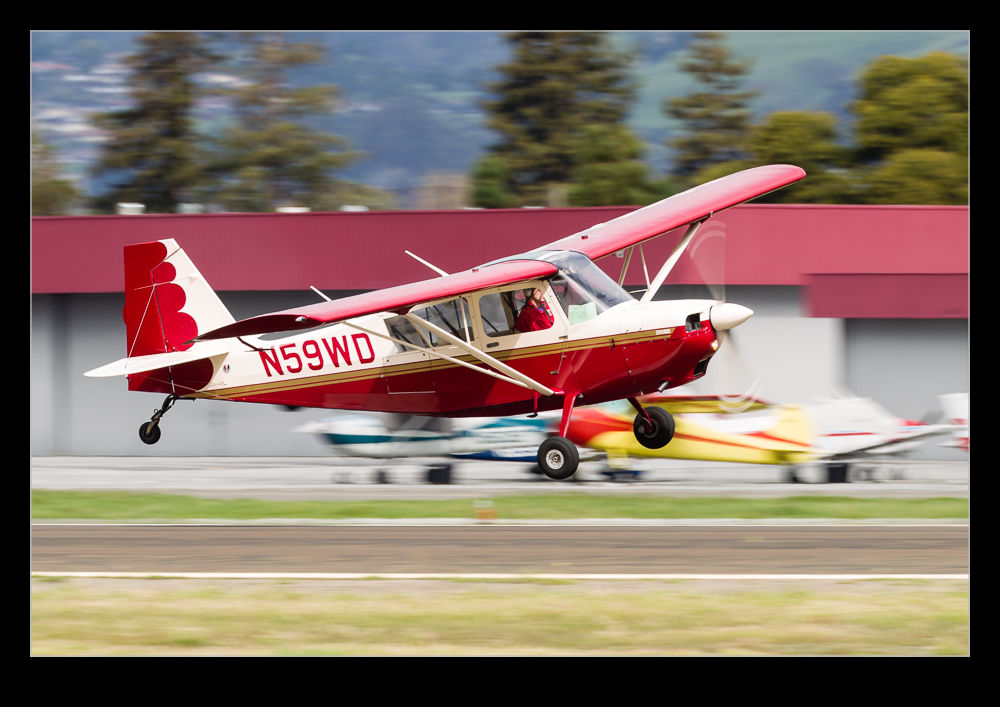
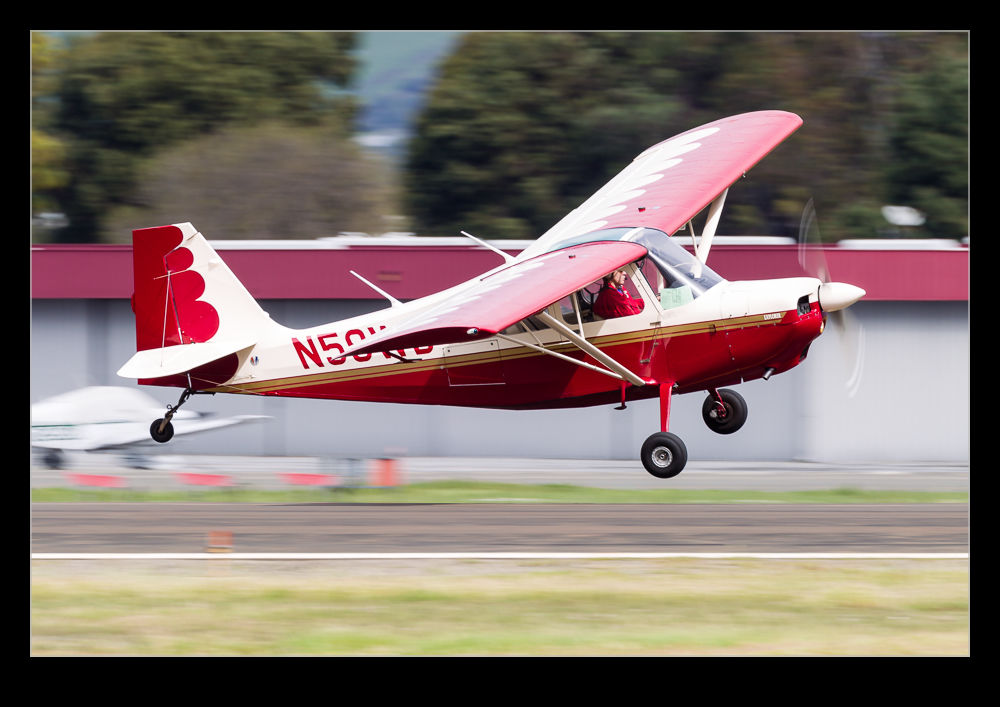 This Citabria was flying circuits at Hayward while I was there. The wind was pretty strong and coming across the runway so the pilot was taking the opportunity to practice their crosswind landings. A lot of wing was down into wind in order to compensate for the conditions and, while they occasionally struggled with some of the bigger gusts, they did seem to have good control of the aircraft. I guess awkward conditions are a reason a lot of flyers would stay on the ground but this one saw an opportunity to get some good practice in. Nicely done!
This Citabria was flying circuits at Hayward while I was there. The wind was pretty strong and coming across the runway so the pilot was taking the opportunity to practice their crosswind landings. A lot of wing was down into wind in order to compensate for the conditions and, while they occasionally struggled with some of the bigger gusts, they did seem to have good control of the aircraft. I guess awkward conditions are a reason a lot of flyers would stay on the ground but this one saw an opportunity to get some good practice in. Nicely done!
An Alternative to Negative Scanning
 I am in the process of experimenting with a new approach to scanning old photographs. For many years I have been using a Minolta Scan Dual III scanner. It can accept strips of negatives or slides and does a reasonable job of scanning them in. It is a bit labor intensive and is certainly not fast. Moreover, the scanner is not terribly reliable and it will often hang mid scan requiring me to restart it and close down the application before restarting that too. Since it takes a long time, I often get it running and go and do something else so I might miss the problem.
I am in the process of experimenting with a new approach to scanning old photographs. For many years I have been using a Minolta Scan Dual III scanner. It can accept strips of negatives or slides and does a reasonable job of scanning them in. It is a bit labor intensive and is certainly not fast. Moreover, the scanner is not terribly reliable and it will often hang mid scan requiring me to restart it and close down the application before restarting that too. Since it takes a long time, I often get it running and go and do something else so I might miss the problem.
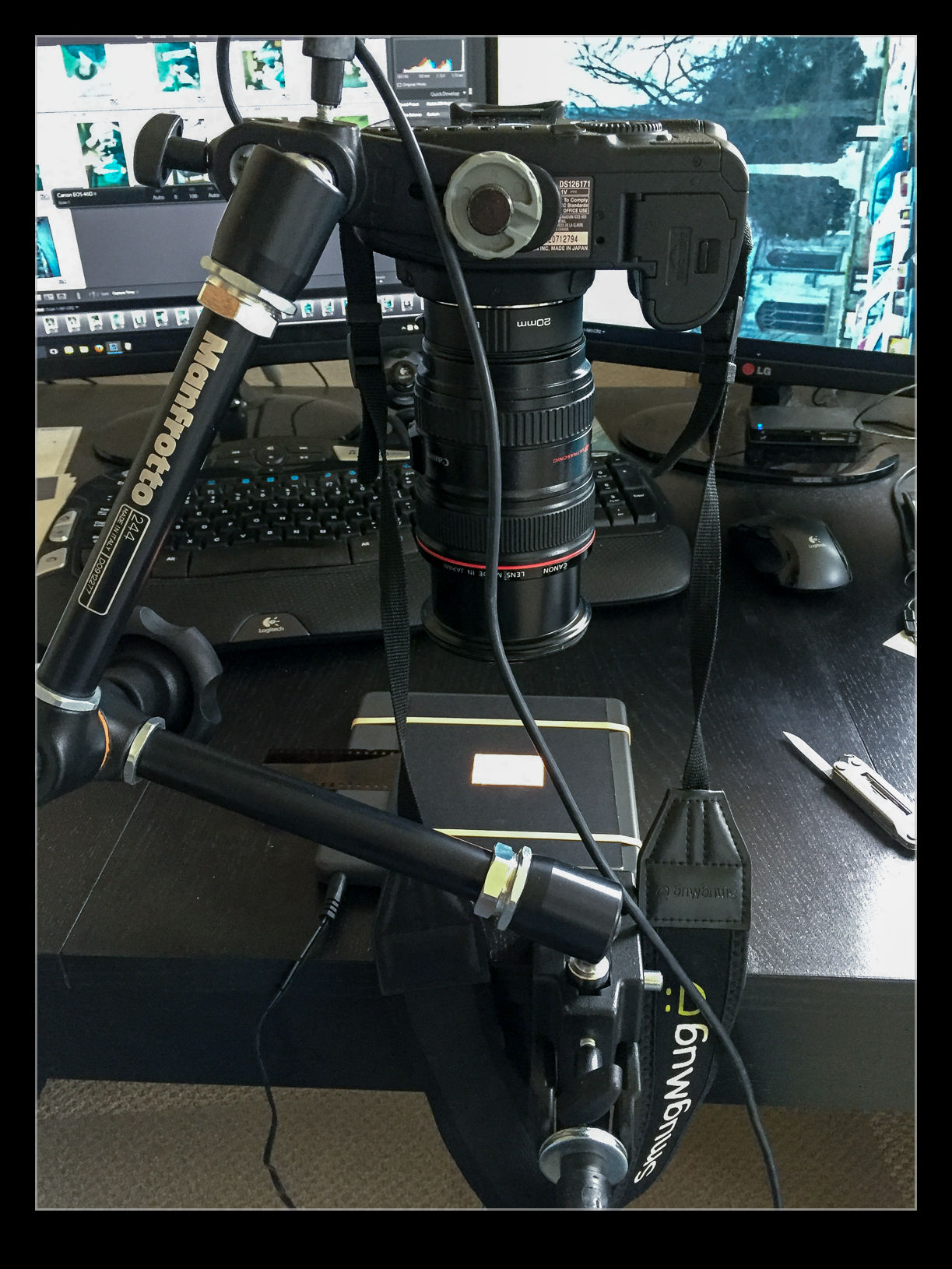
I do have another imaging tool that works very quickly. In fact I have several of them. These are my current digital cameras. I have bought a set of extension tubes to allow me to treat existing lenses as macro lenses. I have also acquired a small light pad. Cutting some card to shape means I can hold down any old negatives and view them through a hole with illumination from the light pad below. Mount a camera on an arm looking down on the pad and I now have a way to image the negative.
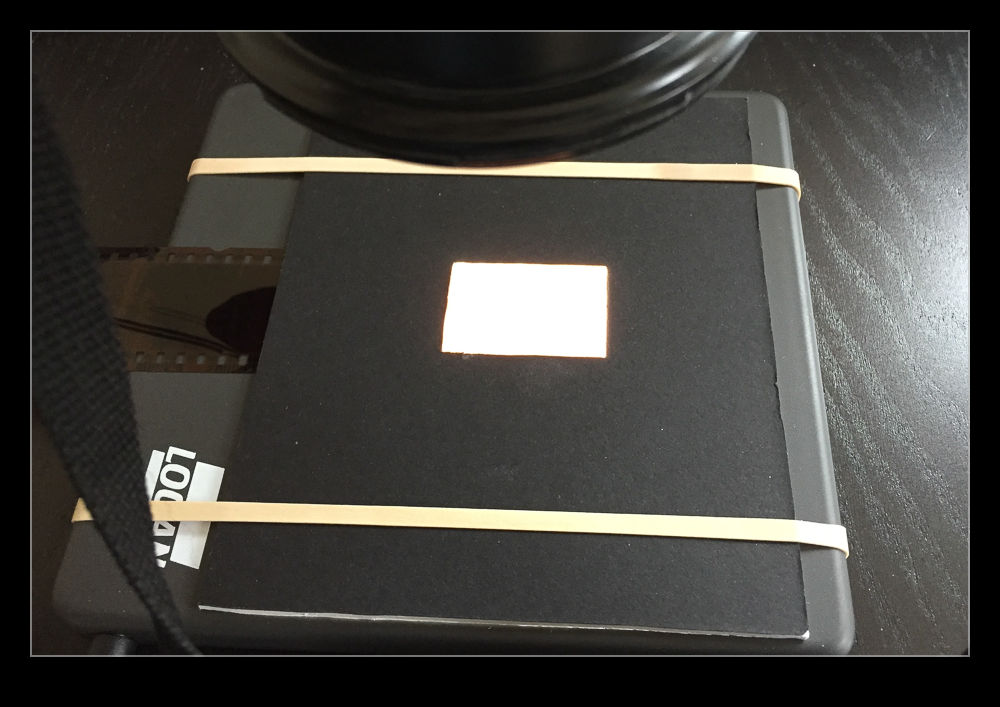 I am taking the images at my desk so I am able to tether the camera to the computer and use Lightroom to capture the images directly. This has actually provided me with an opportunity to drag out one of my older bodies that doesn’t get used anymore. My old 40D has been sitting on a shelf for a long time but it has come back into use for this project. It has more than enough resolution for this task. (Unfortunately, the batteries are now rather old and don’t hold a charge well so I am going to get an AC adapter from Amazon for ten dollars which should free me to scan as much as I want.)
I am taking the images at my desk so I am able to tether the camera to the computer and use Lightroom to capture the images directly. This has actually provided me with an opportunity to drag out one of my older bodies that doesn’t get used anymore. My old 40D has been sitting on a shelf for a long time but it has come back into use for this project. It has more than enough resolution for this task. (Unfortunately, the batteries are now rather old and don’t hold a charge well so I am going to get an AC adapter from Amazon for ten dollars which should free me to scan as much as I want.)
I slide the negative into the holder and check the rough alignment through the viewfinder. Fortunately, although it took me a while to find it, the 40D does have Liveview so I can make use of that to make sure the alignment is right. I use the trigger release in Lightroom’s tether dialog to take the shot to avoid disturbing the setup. If an image needs over or under exposure, I have to remember that it is a negative so I have to use exposure compensation in the opposite sense. The shot is imported straight in the Lightroom when it is taken. The first thing that I need to do is reverse the tone curve to change the negative to a positive. A white balance correction will take out the color cast of the negative and I now have an image to work with. I have a preset for given film types that does this during the import process.
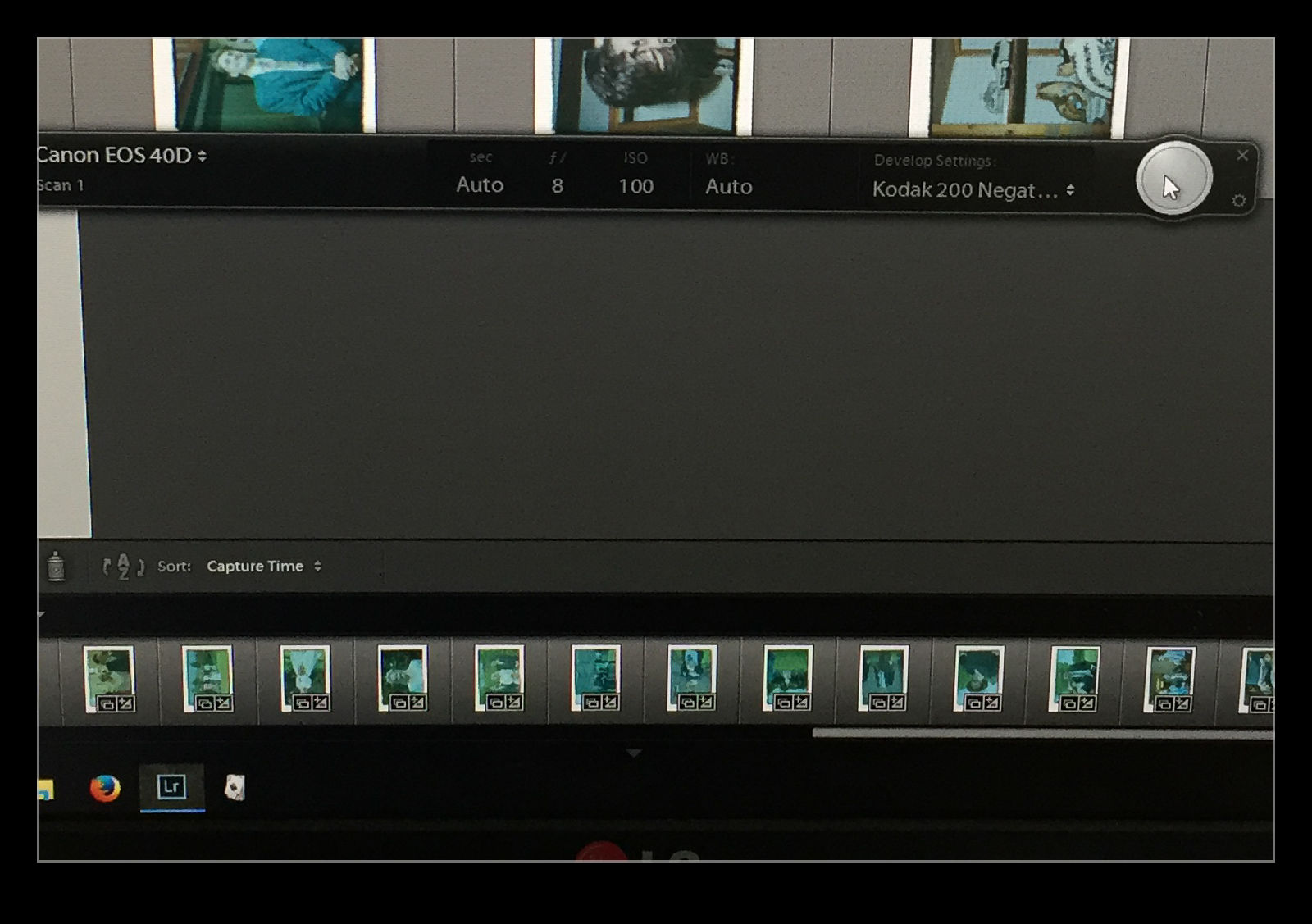 The image is now recognizable but not there yet. Now I have to do some manual manipulation to tidy it up. The sliders have to be used carefully in this case because they are now working in reverse as a result of the tone curve that I applied. This requires some thought. Exposure is still exposure but is reversed. Usually shots look a bit washed out so, what would normally by the Blacks slider is now the Whites. Shadows are handled with the Highlights and vice versa. It takes a bit of getting used to but it is not too hard after some practice. I tried using Auto Tone but it did not do a great job. I imagine the algorithms were not designed for operating in reverse!
The image is now recognizable but not there yet. Now I have to do some manual manipulation to tidy it up. The sliders have to be used carefully in this case because they are now working in reverse as a result of the tone curve that I applied. This requires some thought. Exposure is still exposure but is reversed. Usually shots look a bit washed out so, what would normally by the Blacks slider is now the Whites. Shadows are handled with the Highlights and vice versa. It takes a bit of getting used to but it is not too hard after some practice. I tried using Auto Tone but it did not do a great job. I imagine the algorithms were not designed for operating in reverse!
With everything set up, I can work through a shoot very quickly. Choosing which ones to ignore and reshooting if something doesn’t look right can be done pretty much on the fly. Is the image quality great? It’s okay but not amazing. However, many of the originals are not that great either. For the majority, it actually does a pretty decent job and sets me up for something that I can do more work on if I need to. It is a big improvement on my previous approach and now I will make quick scans when I need them rather than be dreading the time involved and avoiding all but the must have shots to save time.

